The Evolution of Processors in the AI Era: CPU, GPU, NPU
Hello, everyone! Today, as artificial intelligence (AI) technology rapidly advances and becomes deeply integrated into our daily lives, we'll take a look at the history of AI-related processors and their differences. We'll discuss CPU, GPU, and NPU, and delve into why GPUs are better than CPUs for AI tasks, why NPUs are superior to GPUs, and briefly introduce some leading groups and companies in the NPU field.
1.
A brief history of
processors
CPUs have been the backbone of computing systems since the earliest
days of computers. Over time, the need for more specialized processing tasks
arose, leading to the development of GPUs, which were initially designed for
rendering 3D graphics. The versatility of GPUs was eventually discovered, and
they began to be utilized for scientific research, machine learning, and deep
learning tasks. Recently, NPUs have emerged as specialized processors optimized
for AI-related tasks such as deep learning and machine learning.
2. Differences between CPU, GPU, and NPU
|
Processor |
Purpose |
Advantages for AI Tasks |
When |
|
CPU |
General-purpose processing |
Versatile, can handle various tasks |
1960s |
|
GPU |
Graphics rendering, parallel processing |
Thousands of small cores for parallel
processing, faster and more efficient for AI tasks than CPU |
Late 1990s |
|
NPU |
AI-specific operations (deep learning, machine
learning) |
Highly optimized for AI-related tasks, even better
performance than GPU for AI tasks |
Mid-2010s |
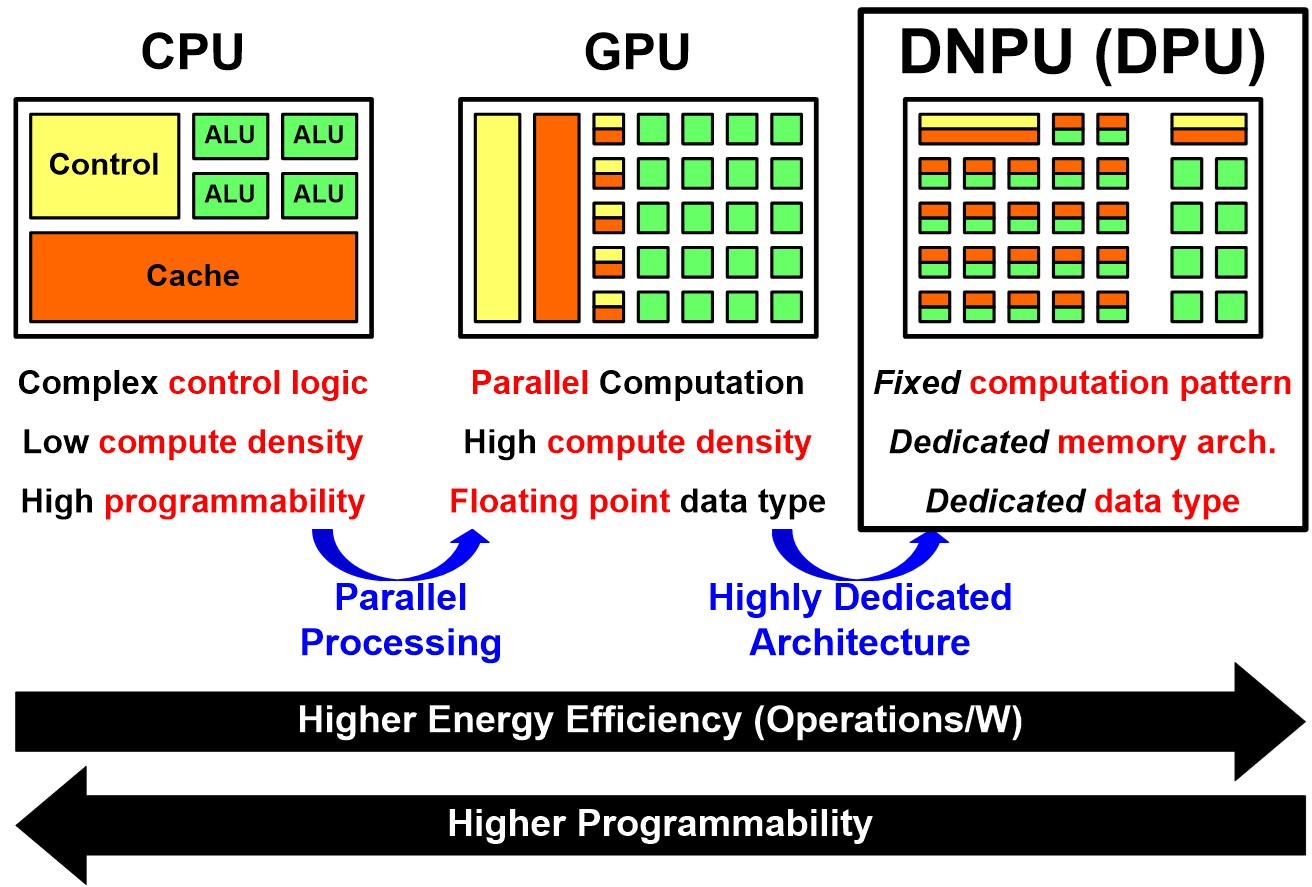
CPU: A general-purpose processor handling a variety of tasks, such as system management, user input, and general programming work.
GPU: Originally designed for 3D graphics rendering, GPUs are now
widely used for data-parallel processing tasks in various fields, including AI,
thanks to their thousands of small cores capable of processing numerous
operations simultaneously.
NPU: A specialized processor designed specifically for artificial
neural network processing. NPUs are optimized for AI operations such as deep
learning and machine learning, providing faster and more efficient processing
compared to traditional CPUs and GPUs.
3.
Why GPUs are better than
CPUs for AI tasks
GPUs excel in parallel processing, making them suitable for AI tasks
that involve processing large amounts of data simultaneously. With thousands of
small cores, GPUs can handle numerous calculations at once, resulting in faster
processing times and better efficiency when compared to CPUs for AI tasks such
as machine learning and deep learning.
4.
Why NPUs are superior to
GPUs
While GPUs are indeed better suited for AI tasks than CPUs, NPUs are
specifically designed for AI operations, making them even more efficient. NPUs
are optimized for tasks such as matrix operations, which are crucial for neural
network processing. This focus on AI-specific tasks allows NPUs to achieve even
better performance than GPUs for deep learning and machine learning
applications.
5. Leading groups and companies in the NPU field
|
Company |
NPU Product/Technology |
Description |
|
NVIDIA |
Tensor Cores |
NPUs integrated into NVIDIA's GPU architectures,
designed for AI acceleration |
|
Google |
Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) |
Custom ASIC designed specifically for
machine learning and deep learning tasks |
|
Apple |
Neural Engine |
NPU integrated into Apple's A-series and M-series
chips, powering AI tasks on iPhones, iPads, and Mac computers |
Conclusion
Understanding the history and differences
between CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs is essential as AI technology continues to evolve
and impact our daily lives. By choosing the right processor for specific tasks,
we can harness the full potential of AI technology and stay ahead in this
rapidly changing world. So, remember to consider CPUs for general computing,
GPUs for parallel processing tasks, and NPUs for AI-specific operations.




Comments
Post a Comment